What Is Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a long-term condition that causes inflammation of the lining of the digestive system. Most commonly, the inflammation affects the last section of the small intestine (ileum) or the large intestine (colon), however, Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the digestive system, from the mouth to the back passage.
Crohn’s disease symptoms
The most common symptoms of Crohn’s disease include:
· Diarrhoea
· Abdominal pain
· Fever
· Extreme tiredness (fatigue)
· Blood and mucus in your stools (faeces)
· Unintended weight loss
If you are suffering the aforementioned symptoms, please contact MyHealthcare Clinic on 0207 099 5555 for a diagnosis and course of treatment from one of our private GPs.
It is possible that people with Crohn’s disease can sometimes go for long periods without any symptoms, or with very mild symptoms, known as remission. Remission can be followed by periods where symptoms flare up and become particularly troublesome.
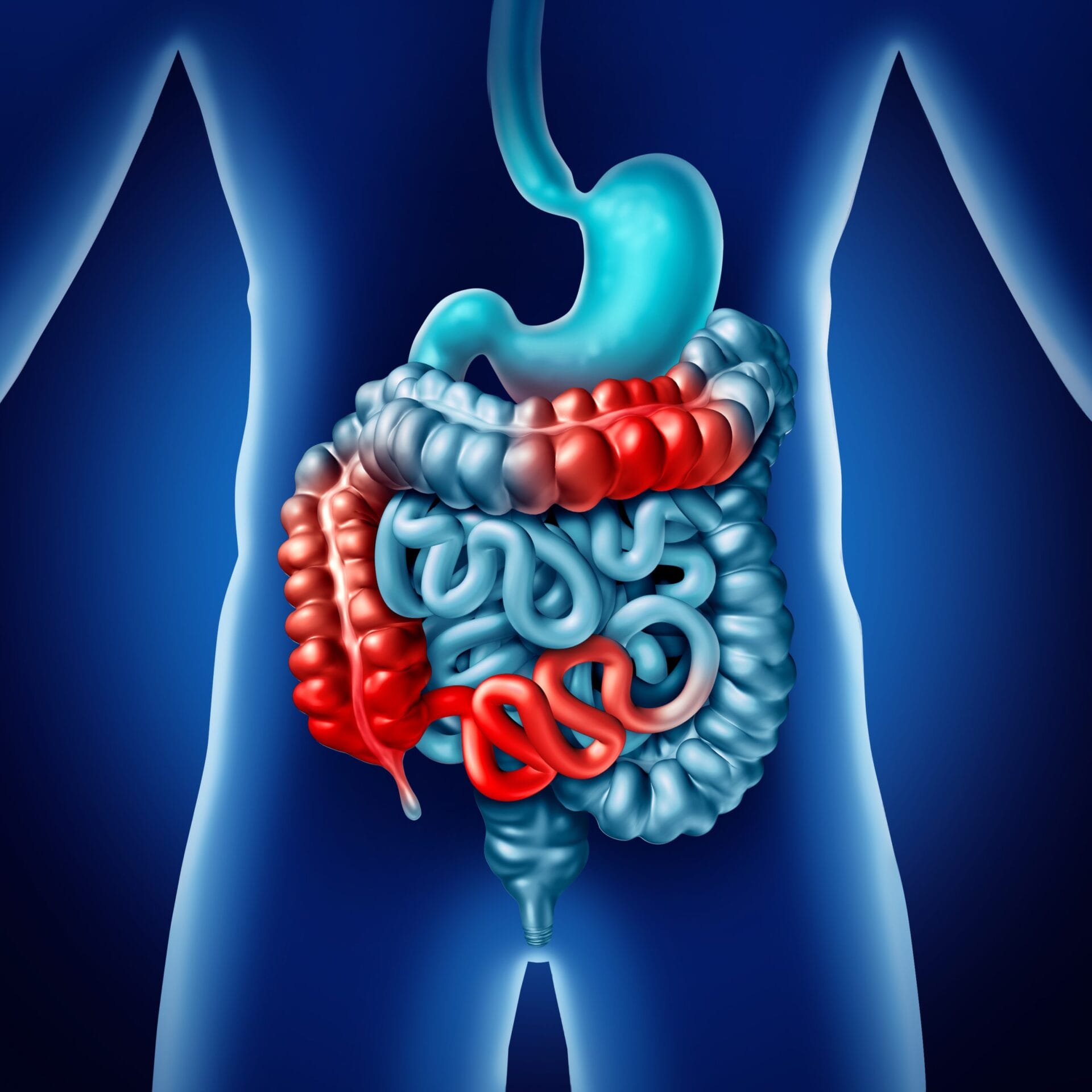
What causes Crohn’s disease?
The precise cause of Crohn’s disease is unknown, however, research suggests a combination of factors may be responsible, such as:
· Genetics – the genes you inherit from your parents may increase your risk of developing Crohn’s disease
· The immune system – the inflammation may be caused by a problem with the immune system (the body’s natural defence against infection and illness) that mistakenly causes it to attack the healthy bacteria in the gut
· Previous infection – a previous infection may trigger this abnormal response from the immune system
· Smoking – smokers with Crohn’s disease usually have more severe symptoms than non-smokers
Crohn’s disease treatment
As there is currently no cure for Crohn’s disease, the aim of treatment is to stop the inflammatory process, and relieve symptoms, by inducing and maintaining remission. The first treatment, prescribed by a GP, to reduce symptoms, is usually steroid medication (corticosteroids). If this doesn’t help, medication to suppress the immune system (immunosuppressants) and medication to reduce inflammation may be prescribed.
In severe cases of Crohn’s disease, surgery may be needed to remove the inflamed section of intestine.
Once your symptoms are under control (in remission), further medication may be needed to help maintain this.
Who is affected by Crohn’s disease?
Crohn’s disease is relatively uncommon, with at least 115,000 people living with the condition in the UK. Crohn’s disease can affect people of all ages, including children, however, most cases first develop between the ages of 16 years old and 30 years old, with a large number of cases developing later in life, between the ages of 60 and 80.
Please contact MyHealthcare Clinic for an appointment with one of our private GPs, if you are suffering the symptoms mentioned.
